Tax Credits, the Distribution of Subsidized Health Insurance Premiums, and the Uninsured
Tax Credits, the Distribution of Subsidized Health Insurance Premiums, and the Uninsured
Introduction: In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the financial aspects of obtaining health insurance have become a focal point. This article explores the intricate relationship between tax credits, the distribution of subsidized health insurance premiums, and the impact on the uninsured population.
Understanding Tax Credits: Tax credits serve as financial incentives provided by the government to ease the burden on individuals seeking health insurance. These credits come in various forms, each designed to alleviate specific financial strains related to healthcare expenses.
Subsidized Health Insurance Premiums: Subsidized health insurance premiums, a cornerstone of healthcare affordability, involve government support to lower the overall cost of insurance for individuals. This subsidy ensures that a broader segment of the population can access necessary healthcare services.
The Link Between Tax Credits and Subsidized Premiums: A symbiotic relationship exists between tax credits and subsidized health insurance premiums. Tax credits act as catalysts, making insurance premiums more manageable and accessible. Case studies reveal the tangible impact of this synergy on individuals' lives.
Benefits for the Insured: Individuals stand to gain significantly from this collaboration. Reduced financial barriers mean more people can afford health insurance, leading to increased coverage and improved overall health outcomes. The accessibility to healthcare services improves, resulting in a healthier and more productive society.
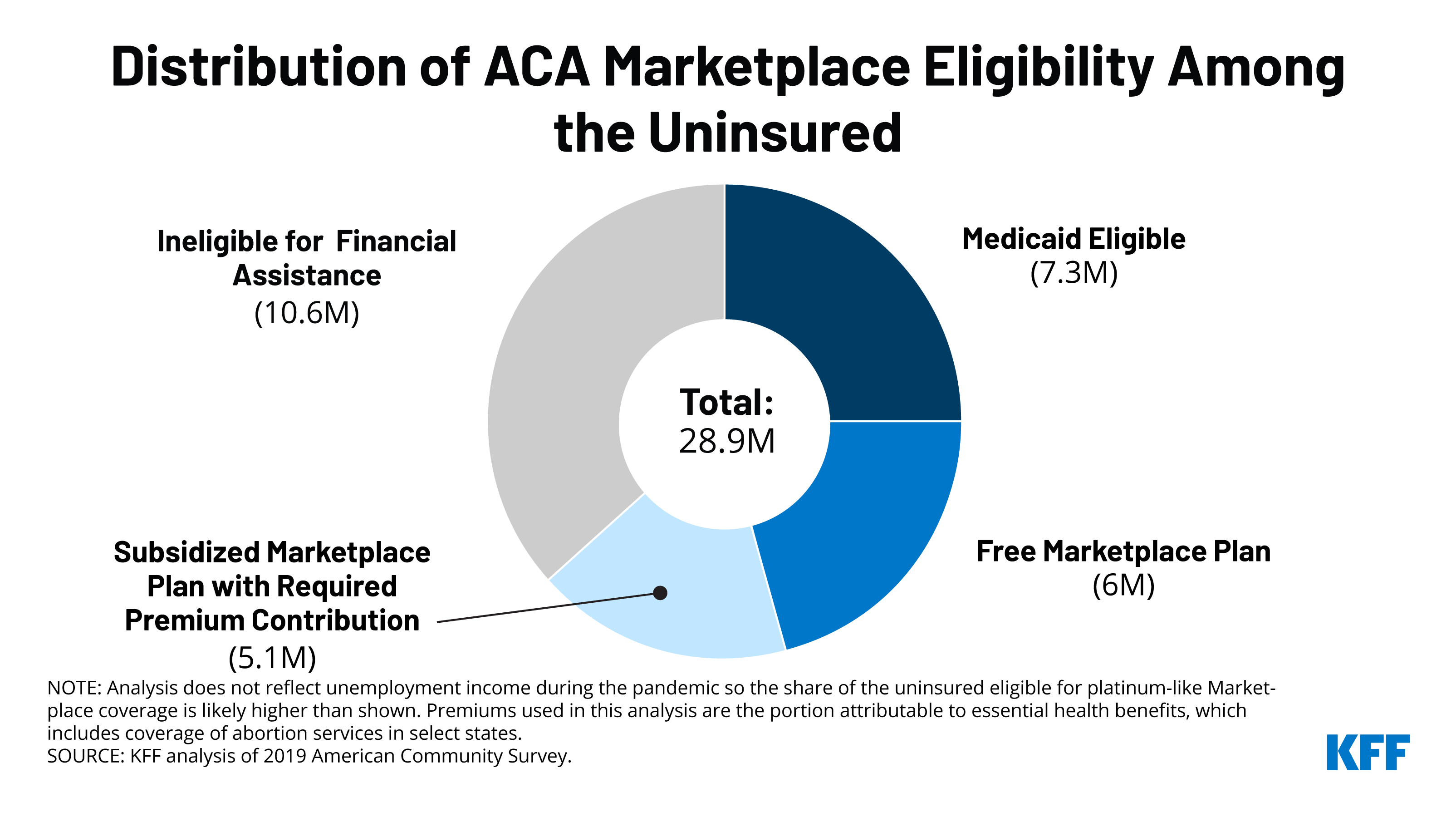
Impact on the Uninsured: Despite these positive developments, a segment of the population remains uninsured. Addressing this issue requires a strategic approach to extend the benefits of tax credits and subsidized premiums to the uninsured, ensuring that no one is left behind.
Policy Considerations: Examining current policies reveals both strengths and areas for improvement. Recommendations include fine-tuning policies to reach underserved populations and fostering collaboration between government agencies and private entities.
Challenges and Solutions: Distribution challenges exist, hindering the effectiveness of tax credits. Solutions involve streamlining processes, enhancing outreach programs, and addressing bureaucratic hurdles to ensure efficient distribution to those who need it most.
Public Awareness: Creating awareness about available benefits is crucial. Initiatives focused on educating the public about tax credits and subsidized health insurance premiums play a pivotal role in increasing enrollment and participation.
Legislative Updates: Recent legislative changes impact the landscape of tax credits and health insurance premiums. Understanding these changes is vital for individuals and businesses alike, as they navigate the evolving terrain of healthcare affordability.
Real-life Stories: Incorporating personal narratives adds depth to the discussion. Real-life stories of individuals positively impacted by tax credits and subsidized premiums humanize the topic, resonating with readers on a personal level.
Future Outlook: Predicting the future of tax credits and subsidized health insurance premiums involves considering emerging trends and potential developments. As technology and policies evolve, so too will the landscape of healthcare affordability.
Comparison with Other Health Insurance Models: Contrasting tax credit-based systems with alternative health insurance models sheds light on the strengths and weaknesses of each approach. Understanding these nuances is essential for policymakers and individuals making informed choices.
Expert Opinions: Insights from experts in the field offer a diverse perspective on the effectiveness of tax credits in addressing healthcare affordability. Expert opinions contribute valuable insights to the ongoing discourse on health insurance accessibility.
What is the Covered California Premium Tax Credit?
The Covered California Premium Tax Credit, often referred to simply as the premium tax credit, is a financial assistance program designed to help individuals and families afford health insurance coverage through the Covered California marketplace. This credit is available to those who purchase their health insurance plans through Covered California and meet certain eligibility criteria based on income and household size.
Qualifying for the Premium Tax Credit
To qualify for the premium tax credit, individuals and families must meet specific income requirements set forth by the Affordable Care Act (ACA). These requirements take into account the individual's or household's modified adjusted gross income (MAGI), which includes income from various sources such as wages, salaries, tips, taxable interest, and certain non-taxable sources like Social Security benefits.
How is the Premium Tax Credit Calculated?
The amount of the premium tax credit is determined based on a sliding scale that considers the individual's or household's income in relation to the federal poverty level (FPL). Generally, individuals and families with lower incomes receive larger credits to help offset the cost of their health insurance premiums.
Do You Have to Pay Back the Premium Tax Credit?
One common question among Covered California enrollees is whether they have to pay back any portion of the premium tax credit received. The answer depends on various factors, including changes in income, family size, and discrepancies between estimated income and actual income reported on the tax return.
Reconciling the Premium Tax Credit on Taxes
At the end of the tax year, individuals who have received advance payments of the premium tax credit must reconcile the amount received with the actual credit they are eligible for based on their annual income. This process occurs when filing taxes using IRS Form 8962.
Repayment Scenarios
Excess Advance Payments
If an individual's actual income exceeds the estimate used to determine the advance premium tax credit, they may have received more financial assistance than they were eligible for. In this case, the excess advance payments must be repaid when filing taxes.
Lower Income than Expected
Conversely, if an individual's actual income is lower than the estimate used to calculate the advance premium tax credit, they may be entitled to a higher credit than originally received. In such instances, they may receive a refund or see a reduction in the amount owed on their taxes.
Exceptions to Repayment
Certain exceptions exist that may waive the requirement to repay excess advance payments of the premium tax credit. These exceptions typically apply to individuals experiencing significant life changes, such as marriage, divorce, birth of a child, or changes in employment status.
Avoiding Repayment
To minimize the likelihood of owing repayment of the premium tax credit, individuals should ensure that their income estimates provided to Covered California are as accurate as possible. Additionally, promptly reporting any changes in income or family circumstances can help adjust advance payments to align with actual eligibility.
Conclusion
The Covered California Premium Tax Credit serves as a valuable resource for individuals and families seeking affordable health insurance coverage. By understanding the eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and potential repayment scenarios associated with the premium tax credit, enrollees can navigate the healthcare marketplace with confidence and financial stability.
In conclusion, the intricate dance between tax credits, subsidized health insurance premiums, and the uninsured population is a dynamic force in shaping the future of healthcare affordability. By addressing challenges, implementing effective policies, and raising public awareness, we pave the way for a healthier and more inclusive society.
FAQs:
How do tax credits directly impact the cost of health insurance premiums?
- Tax credits work by reducing the amount of income tax individuals owe, directly lowering the overall cost of health insurance premiums.
What challenges do policymakers face in ensuring equitable distribution of tax credits?
- Policymakers encounter challenges such as bureaucratic hurdles, inefficient processes, and the need for collaboration between public and private entities.
Are there any eligibility criteria for individuals to benefit from subsidized health insurance premiums?
- Eligibility criteria often include income levels, family size, and other factors that determine financial need.
How can public awareness about tax credits be improved?
- Public awareness can be enhanced through targeted educational campaigns, community outreach programs, and collaborations with healthcare providers.
What role do tax credits play in addressing disparities in healthcare access?
- Tax credits play a crucial role in reducing financial disparities, making healthcare more accessible to a broader segment of the population.



Comments
Post a Comment